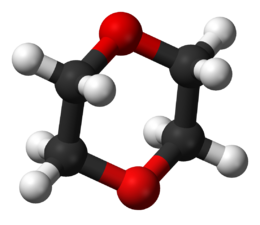
1,4-Dioxane
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dioxane
|
|||
| Other names
1,4-Dioxacyclohexane
[1,4]Dioxane p-Dioxane [6]-crown-2 Diethylene dioxide Diethylene ether Dioxan |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
CAS Number
|
|
||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
||
|
Beilstein Reference
|
102551 | ||
| ChEBI |
|
||
| ChEMBL |
|
||
| ChemSpider |
|
||
| DrugBank |
|
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.239[42] | ||
| EC Number | 204-661-8 | ||
| KEGG |
|
||
|
PubChemCID
|
|
||
| RTECS number | JG8225000 | ||
| UNII |
|
||
| UN number | 1165 | ||
|
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
||
|
InChI
|
|||
|
SMILES
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 88.106 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | Mild, ether-like[1] | ||
| Density | 1.033 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 11.8 °C (53.2 °F; 284.9 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 101.1 °C (214.0 °F; 374.2 K) | ||
|
Solubility in water
|
Miscible | ||
| Vapor pressure | 29 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
|
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
|
−52.16·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std molar entropy(S
|
196.6 J/K·mol | ||
|
Std enthalpy of formation(ΔfH⦵298)
|
−354 kJ/mol | ||
|
Std enthalpy of combustion(ΔcH⦵298)
|
−2363 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Carcinogen[1] | ||
| GHS pictograms |    |
||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
|
GHS hazard statements
|
H225,H315,H319,H332,H336,H351,H370,H372,H373 | ||
|
GHS precautionary statements
|
P201,P202,P210,P233,P240,P241,P242,P243,P260,P261,P264,P270,P271,P280,P281,P302+352,P303+361+353,P304+312,P304+340,P305+351+338,P307+311,P308+313,P312,P314,P321 | ||
| NFPA 704 |
 3
2
1
|
||
| Flash point | 12 °C (54 °F; 285 K) | ||
|
Autoignition temperature
|
180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2.0–22%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50(median dose)
|
|
||
|
LC50(median concentration)
|
|
||
|
LCLo(lowest published)
|
1000–3000 ppm (guinea pig, 3 hr) 12,022 ppm (cat, 7 hr) 2085 ppm (mouse, 8 hr)[2] |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm (360 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 1 ppm (3.6 mg/m,3) [30-minute][1] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [500 ppm][1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Oxane Trioxane Tetroxane Pentoxane |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
1,4-Dioxane(/daɪˈɒkseɪn/) is a heterocyclic organic compound, classified as an ether. It is a colorless liquid with a faint sweetodorsimilar to that of diethyl ether. The compound is often called simplydioxanebecause the other dioxane isomers (1,2- and 1,3-) are rarely encountered.
Dioxane is used as a solvent for a variety of practical applications as well as in the laboratory, and also as a stabilizer for the transport of chlorinated hydrocarbons in aluminum containers.[3]
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dioxane
|
|||
| Other names
1,4-Dioxacyclohexane
[1,4]Dioxane p-Dioxane [6]-crown-2 Diethylene dioxide Diethylene ether Dioxan |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
CAS Number
|
|
||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
||
|
Beilstein Reference
|
102551 | ||
| ChEBI |
|
||
| ChEMBL |
|
||
| ChemSpider |
|
||
| DrugBank |
|
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.239[42] | ||
| EC Number | 204-661-8 | ||
| KEGG |
|
||
|
PubChemCID
|
|
||
| RTECS number | JG8225000 | ||
| UNII |
|
||
| UN number | 1165 | ||
|
CompTox Dashboard(EPA)
|
|
||
|
InChI
|
|||
|
SMILES
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 88.106 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | Mild, ether-like[1] | ||
| Density | 1.033 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 11.8 °C (53.2 °F; 284.9 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 101.1 °C (214.0 °F; 374.2 K) | ||
|
Solubility in water
|
Miscible | ||
| Vapor pressure | 29 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
|
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
|
−52.16·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std molar entropy(S
|
196.6 J/K·mol | ||
|
Std enthalpy of formation(ΔfH⦵298)
|
−354 kJ/mol | ||
|
Std enthalpy of combustion(ΔcH⦵298)
|
−2363 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Carcinogen[1] | ||
| GHS pictograms |    |
||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
|
GHS hazard statements
|
H225,H315,H319,H332,H336,H351,H370,H372,H373 | ||
|
GHS precautionary statements
|
P201,P202,P210,P233,P240,P241,P242,P243,P260,P261,P264,P270,P271,P280,P281,P302+352,P303+361+353,P304+312,P304+340,P305+351+338,P307+311,P308+313,P312,P314,P321 | ||
| NFPA 704 |
 3
2
1
|
||
| Flash point | 12 °C (54 °F; 285 K) | ||
|
Autoignition temperature
|
180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2.0–22%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50(median dose)
|
|
||
|
LC50(median concentration)
|
|
||
|
LCLo(lowest published)
|
1000–3000 ppm (guinea pig, 3 hr) 12,022 ppm (cat, 7 hr) 2085 ppm (mouse, 8 hr)[2] |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm (360 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 1 ppm (3.6 mg/m,3) [30-minute][1] | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [500 ppm][1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Oxane Trioxane Tetroxane Pentoxane |
||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Synthesis
Dioxane is produced by the acid-catalysed dehydration of diethylene glycol, which in turn is obtained from the hydrolysis of ethylene oxide.
Structure
The dioxane molecule is centrosymmetric, meaning that it adopts a chair conformation, typical of relatives of cyclohexane. However, the molecule is conformationally flexible, and the boat conformation is easily adopted, e.g. in the chelation of metal cations. Dioxane resembles a smaller crown ether with only two ethyleneoxyl units.
Uses
Trichloroethane transport
In the 1980s, most of the dioxane produced was used as a stabilizer for 1,1,1-trichloroethane for storage and transport inaluminiumcontainers. Normally aluminium is protected by a passivating oxide layer, but when these layers are disturbed, the metallic aluminium reacts with trichloroethane to give aluminium trichloride, which in turn catalyses the dehydrohalogenation of the remaining trichloroethane to vinylidene chloride and hydrogen chloride. Dioxane “poisons” this catalysis reaction by forming an adduct with aluminum trichloride.[4]
As a solvent
Binary phase diagram for the system 1,4-dioxane/water
Dioxane is used in a variety of applications as a versatile aprotic solvent, e. g. for inks, adhesives, and cellulose esters.[6]It is substituted for tetrahydrofuran (THF) in some processes, because of its lower toxicity and higher boiling point (101 °C, versus 66 °C for THF).
While diethyl ether is rather insoluble in water, dioxane is miscible and in fact is hygroscopic. At standard pressure, the mixture of water and dioxane in the ratio 17.9:82.1 by mass is a positive azeotrope that boils at 87.6 C.[7]
The oxygen atoms are Lewis-basic, and so dioxane is able to solvate many inorganic compounds and serves as a chelating diether ligand. It reacts with Grignard reagents to precipitate the magnesium dihalide. In this way, dioxane is used to drive the Schlenk equilibrium.[4]Dimethylmagnesium is prepared in this manner:[8][9]
- 2 CH3MgBr + (C2H4O)2→ MgBr2(C2H4O)2
- (CH
Spectroscopy
Dioxane is used as an internal standard for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in deuterium oxide.[10]
Toxicology
Safety
Dioxane has an LD50 of 5170 mg/kg in rats.[4]This compound is irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract. Exposure may cause damage to the central nervous system, liver and kidneys.[11]In a 1978 mortality study conducted on workers exposed to 1,4-dioxane, the observed number deaths from cancer was not significantly different from the expected number.[12]Dioxane is classified by the National Toxicology Program as “reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen”.[13]It is also classified by the IARC as a Group 2B carcinogen:possibly carcinogenic to humansbecause it is a known carcinogen in other animals.[14]TheUnited States Environmental Protection Agencyclassifies dioxane as a probable human carcinogen (having observed an increased incidence of cancer in controlled animal studies, but not in epidemiological studies of workers using the compound), and a known irritant (with a no-observed-adverse-effects level of 400 milligrams per cubic meter) at concentrations significantly higher than those found in commercial products.[15]Under California Proposition 65, dioxane is classified in the U.S. State of California to cause cancer.[16]Animal studies in rats suggest that the grea health risk is associated with inhalation of vapors in the pure form.[17][18][19]
Explosion hazard
Like some other ethers, dioxane combines with atmospheric oxygen upon prolonged exposure to air to form potentially explosive peroxides.Distillationof dioxanes concentrates these peroxides, increasing the danger.
Environment
Dioxane has affected groundwater supplies in several areas. Dioxane at the level of 1 μg/L (~1 ppb) has been detected in many locations in the US.[5]In the State of New Hampshire alone in 2010 it had been found at 67 sites, ranging in concentration from 2 ppb to over 11,000 ppb. Thirty of these sites are solid waste landfills, most of which have been closed for years. It also has low toxicity to aquatic life and can be biodegraded via a number of pathways.[20]The problems are exacerbated since dioxane is highly soluble in water, does not readily bind to soils, and readily leaches to groundwater. It is also resistant to naturally occurring biodegradation processes. Due to these properties, a dioxane plume can be larger (and further downgradient) than the associated solvent plume.
Cosmetics
As a byproduct of the ethoxylation process, a route to some ingredients found in cleansing and moisturizing products, dioxane can contaminate cosmetics and personal care products such as deodorants, perfumes, shampoos, toothpastes and mouthwashes.[21][22]The ethoxylation process makes the cleansing agents, such as sodium laureth sulfate and ammonium laureth sulfate, less abrasive and offers enhanced foaming characteristics. 1,4-Dioxane is found in small amounts in some cosmetics, a yet unregulated substance used in cosmetics in both China and the U.S.[23]
Since 1979 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have conducted s on cosmetic raw materials and finished products for the levels of 1,4-dioxane.[24]1,4-Dioxane was present in ethoxylated raw ingredients at levels up to 1410 ppm (~0.14%wt), and at levels up to 279 ppm (~0.03%wt) in off the shelf cosmetic products.[24]Levels of 1,4-dioxane exceeding 85 ppm (~0.01%wt) in children’s shampoos indicate that close monitoring of raw materials and finished products is warranted.[24]While the FDA encourages manufacturers to remove 1,4-dioxane, it is not required by federal law.[25]
See also
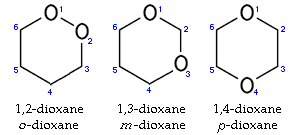
The three isomers of dioxane
-
1,2-Dioxane
-
1,3-Dioxane
-
Dioxolane
-
9-crown-3
-
Crown ether
-
Dioxane tetraketone
-
Oxalic anhydride
-
Sodium laureth sulfate
-
Dioxanone